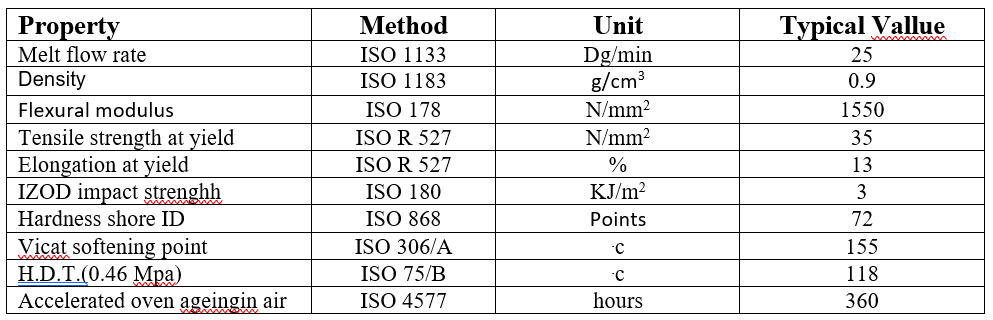
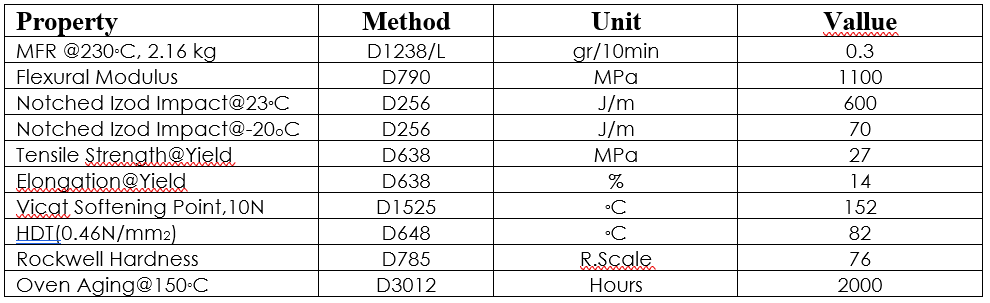
Polymers play an important role in various industries, and polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are among the most widely used thermoplastic polymers. Although these two polymers have similarities in appearance and some physical properties, they have fundamental differences in chemical structure, mechanical properties, applications, and production process. In this article, we will comprehensively review the differences between polyethylene and polypropylene.
Review of the differences between polyethylene and polypropylene
1. Chemical structure
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is obtained from the polymerization of the monomer ethylene (C₂H₄). This polymer is divided into different types depending on the type of polymerization:
LDPE (low density): has a branched, soft, and flexible structure.
HDPE (High Density): Has a linear and stiffer structure
LLDPE: Linear structure with short branches that combines the properties of LDPE and HDPE.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is obtained from the polymerization of the monomer propylene (C₃H₆). In its structure, a methyl group is attached to each monomer unit, which makes it stiffer, more transparent and more thermally stable than polyethylene. PP is produced in three types: isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic, with isotactic being the most widely used.
2. Production and forming process
Both polymers are processed using similar methods such as extrusion, injection, blow molding and rotational molding. However, due to differences in melting temperature and viscosity, their operating parameters are different.
PE: Processed at a lower temperature and has higher flowability
PP: Requires higher temperatures and may take longer to mold, but has better surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
3. Durability and Environmental Stability
Both polyethylene and polypropylene are resistant to chemicals and moisture. However, they may degrade under UV light and high temperatures unless stabilizing additives are used.
Polyethylene generally degrades more rapidly under sunlight.
Polypropylene is more heat resistant but becomes more brittle in the cold.
4. Applications
Polyethylene applications:
Packaging (nylon, plastic bags)
Food bottles and containers
Plumbing (water supply, sewage)
Electrical cable insulation
Toys and agricultural equipment
Polypropylene applications:
Automotive interior parts
Household appliances (microwave containers, lids)
Medical equipment (syringes, IV tubing)
Carpets and woven fabrics
Hot or liquid food packaging
5. Biocompatibility and recycling
Both polymers are recyclable, but their recycling processes are different. PE's recycling code is usually (HDPE) 2# or (LDPE) 4#, while PP has a code of 5#.
Polyethylene (especially HDPE) is recycled in more countries.
Polypropylene is recyclable, but less recycled than PE due to processing complexity and contamination.
6. Advantages and Disadvantages
Polyethylene
Advantages:
High impact resistance
Good flexibility
Easy processability
Disadvantages:
Low temperature resistance
Low hardness
Polypropylene
Advantages:
High heat resistance
Greater strength and stiffness
The lightest common thermoplastic
Disadvantages:
Brittleness at low temperatures
Less resistance to UV rays
7. Economic Comparison
Economically, both polymers have relatively low production costs, but there are also differences:
Polyethylene, due to its higher consumption in general industries (such as packaging), usually has a larger volume in terms of the global market. Its price varies depending on whether it is LDPE or HDPE.
Polypropylene, due to its higher technical properties, is used in more industrial applications (for example, automotive parts or medical equipment). Its price is usually slightly higher than PE, but its better performance can provide a better economic justification in some situations.
8. Resistance to chemicals
Both polymers have high chemical resistance, but there are differences:
PE is very resistant to acids, bases, alcohols and salts. However, it is weak against strong oxidizing agents and some aromatic hydrocarbons.
PP is also resistant to most solvents and performs better against fats and oils, making it very suitable for packaging fatty foods.
9. Optical and appearance properties
Polyethylenes, especially LDPE, are usually translucent and have a smooth appearance. In contrast, polypropylene can be more transparent and have a glossier surface. Hence, PP is more popular in applications such as food containers and more luxurious packaging.
10. Thermal and thermal behavior
As mentioned, the melting point of polypropylene is higher than that of polyethylene. This makes PP preferable in environments that require higher temperature resistance, such as microwave containers or car engine parts. Polyethylene softens and loses its shape at high temperatures.
11. Choice in Engineering Design
In engineering design, the choice between PE and PP depends on the functional requirement:
For applications where flexibility, toughness, and high impact resistance are required, polyethylene is more suitable.
For applications where strength, dimensional stability, and heat resistance are important, polypropylene is a better choice.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the choice between polyethylene and polypropylene depends on the application requirement. If greater flexibility and impact resistance are desired, polyethylene is a good choice. Conversely, if greater temperature resistance and hardness are required, polypropylene is a better choice. Both materials are widely used in various industries from packaging to automotive due to their abundance, reasonable price, and high processability.
For more information, you can get our address and contact number through the contact us page.
Related articles:
What is polyethylene?/www.wci-polimer.com
Polypropylene (pp)/www.wci-polimer.com
- ۰ ۰
- ۰ نظر